The Core Web Vitals Algorithm – Website Quality as One of the Ranking Factors

Recently Google announced that it was working on a new algorithm supposed to evaluate how user-friendly a given website is. This means that the search engine position of a page which hasn’t been received well by users can be decreased. Although the algorithm is planned to be implemented in 2021 at the earliest, in today’s entry you can learn what factors it’ll take into account.
Website quality – what is it?
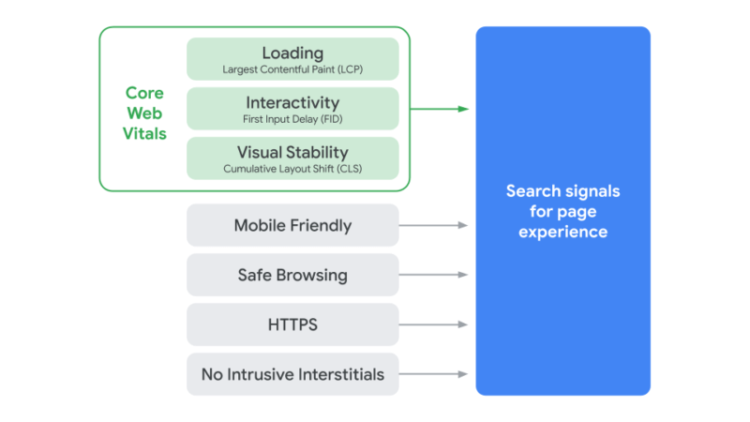
As explained in the Google Search guide, website quality is assessed with the use of Core Web Vitals meaning factors that measure the actual user experience in terms of website loading time, interactivity, or visual stability. Moreover, the already existing factors such as mobile-friendliness, search security, HTTPS and lack of intrusive elements are also taken into account.
Core Web Vitals – a short introduction
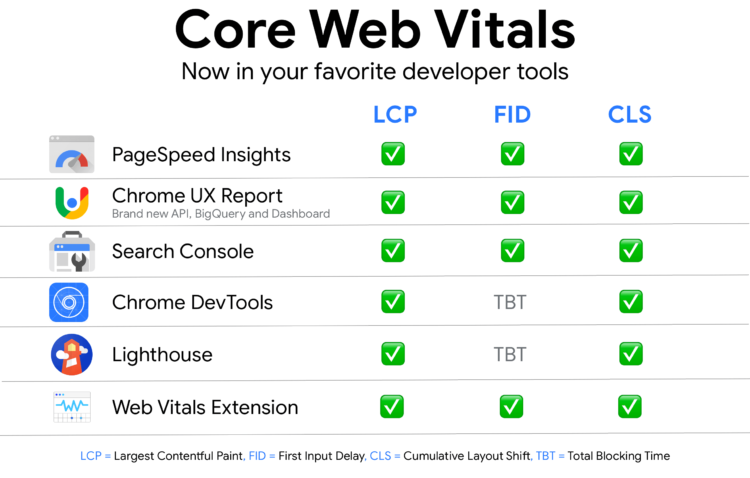
Core Web Vitals are measurable factors that address the user experience of the site and include:
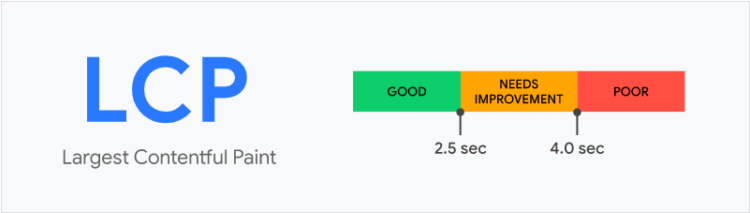
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – measures the time it takes to load the biggest element (it can be both text and graphic/video content) on the website. LCP shouldn’t take more than 2.5 seconds (from the very moment when the page starts loading).
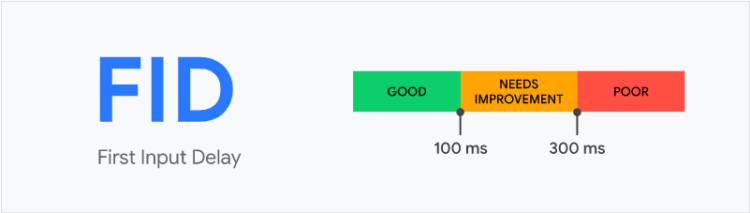
2. First Input Delay (FID) – means the time that passes from the moment the user interacts with the site (i.e. clicks on a link or button) to the moment when the browser actually responds to this interaction. The FID shouldn’t be longer than 100 milliseconds.
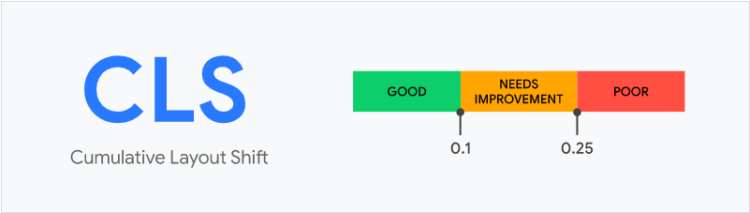
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – measures all the changes of the page layout during the visit. A layout change occurs each time a visible item changes its position. In order to be ranked high on Google, the page needs to keep this indicator at 0.1.
Other factors influencing website quality
Apart from Core Web Vitals, website quality is affected by numerous other factors you’re already familiar with. The list includes:
- Mobile-friendliness – if you want to check whether your site is mobile-friendly, go to Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Search security – monitors whether there are any security issues on your website (e.g. malware). The Security Issues report is available in Google Search Console.
- HTTPS – analyzes whether the HTTPS protocol on your website is implemented correctly.
- No intrusive elements that hinder browsing (these include, for example, aggressive pop-ups, especially those that cover the entire website content on mobile devices).
All the abovementioned elements together with Core Web Vitals affect how qualitative the website is from the users’ perspective. However, each of the factors is characterized by a diverse level of significance and impacts Google algorithms differently.
Website optimization vs. page experience
As it’s been already mentioned, the algorithm is planned to be implemented in 2021, however, you can take advantage of available solutions and tools to start improving your website today. So what can you do now?
- Check out which tools can help you measure LCP, FID, and CLS. This will indicate which of your website elements need to be improved. To learn more about tools for measuring Core Web Vitals, go to web.dev. You can also check the Core Web Vitals report available in Google Search Console.
- See whether your website is adapted to mobile devices.
- Check the Google Search Console report for any security issues.
- Monitor the security of your site’s connection.
- Make sure that your website doesn’t contain any elements that hinder the browsing experience or annoy users.
For the time being, it’s not clear when the algorithm will be implemented, the exact date will be announced six months in advance. No one knows how many pages will be affected by the update and how it’ll change the search engine rankings. However, one can be stated for sure, websites that provide valuable content will be ranked higher, even if their page experience is far from being impeccable.