rel = canonical. What is Canonical URL?

Duplicate content has never been appreciated, neither in the real, nor in the online world. Google robots detect any illegitimate content fast and may impose a manual penalty on websites that don’t live up to the standards. This, in turn, may lead to a significant decrease in the search engine rankings. That’s two steps from a heavy traffic loss. One way to fight on-site content duplication is canonicalization. Can canonical tags be applied on your website and how to benefit from them? Keep reading!
Table of contents:
- What is a Canonical Tag?
- What is Duplicate Content and How to Check If You Have One?
- Why is Rel Canonical Important for SEO?
- How to Implement Canonical Tags Properly?
- Canonical URL – Best Practices
- Rel Canonicals – Common Mistakes
- When Are Canonical Links Not a Necessity?
- What is Rel Canonical – The Takeaway
Regardless of the type – be it a business one-page, or e-commerce – your website can have internal duplicate content issues. That occurs anytime the same or very similar content is found on several pages within one site. Generally speaking, it’s best to simply avoid such situations, but webmasters don’t always have full control over it. This is where canonical tag comes in handy — it simply refers Google, Yahoo, or Bing crawlers to the URL with original (canonical) content, rendering the rest overt duplications.
What is a Canonical Tag?
A canonical tag is an HTML tag inserted in the <head> section of your website code. It’s also referred to as rel canonicals or rel=canonicals.
These elements are used mainly to inform Google robots that specific URLs are master copies of the website. From the search engine’s standpoint, it’s best if every single page with duplicate content is linked to only one canonical URL. However, this isn’t always possible. Thanks to rel canonicals, you’re able to avoid negative consequences of internal duplicate content, as these tags allow you to specify which version of your website is the “preferred” one.
What is Duplicate Content and How to Check if You Have One?
Duplicate content is defined as content that appears in more than one location on various websites. It’s possible to distinguish both internal and external duplicate content.
As you probably know, Google pays great attention to the uniqueness of published content, therefore, if you want to reach top positions in the search results, you need to make sure that your website is filled with unique, quality texts that correspond to specific users’ queries.
How to check if your website has duplicate content? If you don’t want to benefit from any tools, simply copy a few words from your text (e.g., 10 words or two sentences) and paste them into the search box in quotation marks. This way, you’ll quickly see if there are websites with the same content.
If you want to learn more about dealing with duplicate content, read our article: https://delante.co/content-duplication-how-to-deal-with-this-issue/.
Apart from that, there are a few free tools that can help you quickly and effortlessly determine the percentage of duplicate content on your page:
- Copyscape
- Plagspotter
- Duplichecker
- SiteLiner
- Smallseotools
With these solutions, you’ll be able to analyze your website content with a few clicks.
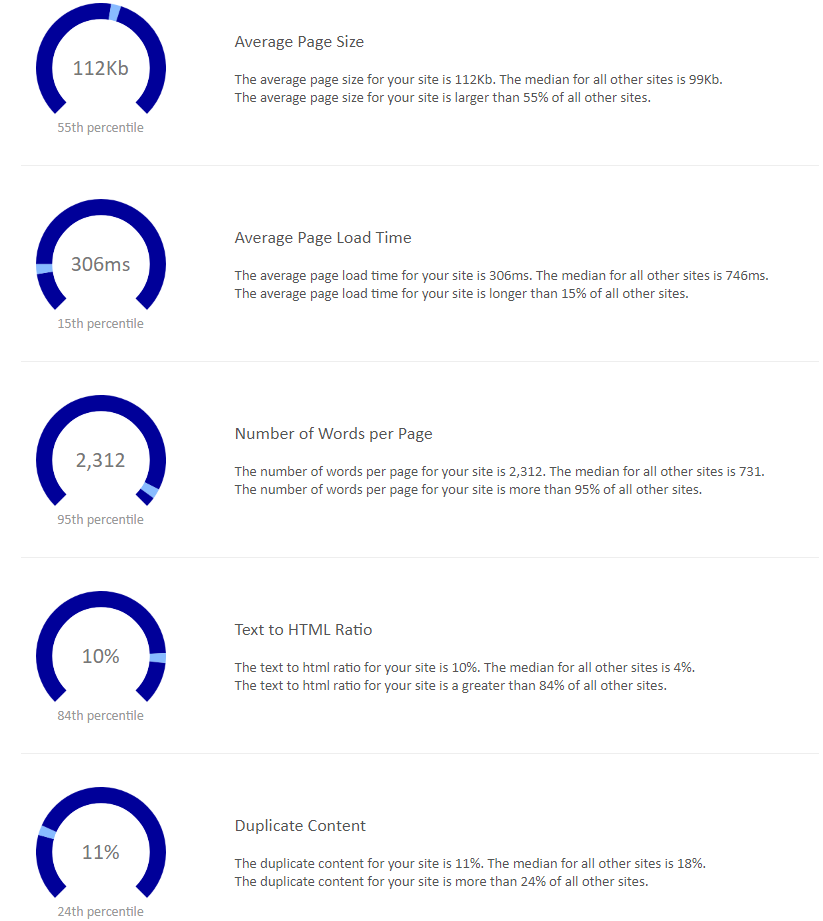
SiteLiner Step by Step
Although we have mentioned a few tools that may come in handy when checking your duplicate content, today, we’ll take a closer look at SiteLiner – an extremely intuitive solution that will take your content strategy to the next level.
To check your duplicate content, simply enter its URL in the search bar and click Go.
Then, you’ll see a detailed graph showing your duplicate content (you can also juxtapose it with other websites), the average website loading time, page size, and many, many more.
Why is Rel Canonical Important for SEO?
Canonical tags are crucial for your SEO process. You may not use them if you don’t want to, but they help the search engine to determine what’s the original content, and what’s only a copy. These solutions have numerous advantages, however, the most popular ones include:
- Properly implemented on-site canonical tags decrease your internal duplicate content which, in turn, helps you improve your positions in the rankings,
- Thanks to rel=canonicals, search engine crawlers are able to quickly determine valuable content. Because of that, your page is processed and indexed faster,
- Unique website content boosts your Page Authority,
- You gain more control over URLs displayed in the search results to users.
Therefore, if your internal duplicate content is high and you want to improve your website parameters and positions, it’s definitely worth using rel canonical tags.
How to Implement Canonical Tags Properly?
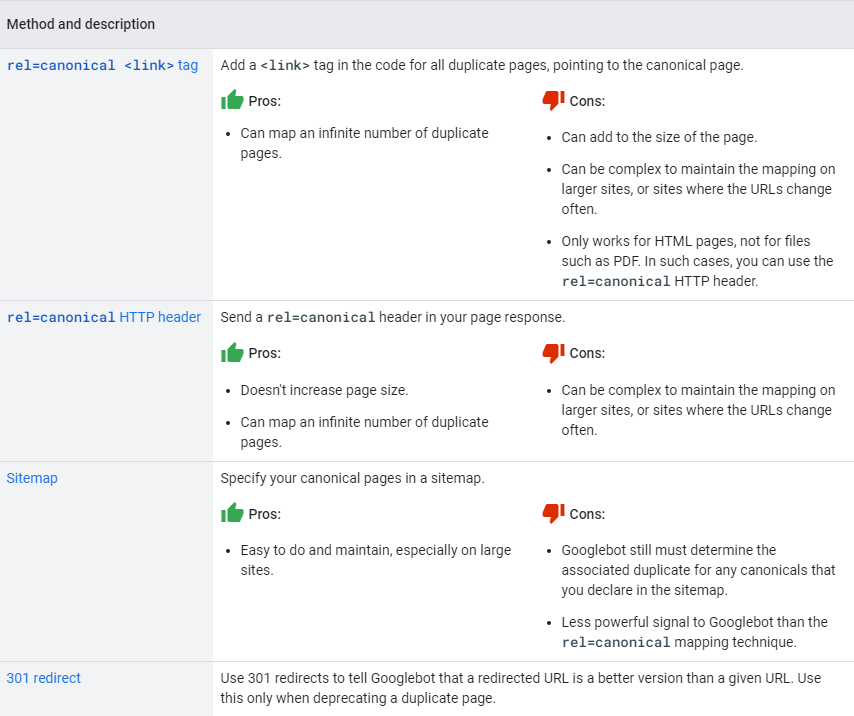
HTML Tags (rel=canonical)
Although this method may seem daunting to those who aren’t particularly computer-literate, applying the rel=canonical tag in the page header is the most popular method of implementing canonicals.
This method varies depending on your CMS, therefore, if you aren’t sure how to proceed, it’s best to contact a specialist company that will support you.
HTTP Headers
Apart from the canonical tags, you may also implement rel canonical HTTP headers.
This solution comes in handy if you need to determine which URL is the canonical one for documents in different forms (not HTML), such as PDF.
To benefit from this solution, you need your site’s .htaccess file, and then you can implement the canonical tag using the following code:
<Files “file-to-canonicalize.pdf”>
Header add Link “< http://www.website.com/canonical-page/>; rel=\”canonical\””
</Files>
301 Redirects
According to Google, it’s possible to use 301 redirects to determine your preferred URLs.
However, it needs to be mentioned that creating a 301 redirect means that actually, only the canonical link will exist, as other versions will simply send users to it.
301 redirects are recommended to deal with duplicate content across:
- HTTPS and HTTP
- WWW and no WWW
- URLs with and without Trailing-Slash
However, before implementing any changes, it’s always worth consulting specialists to see which option will work best in your case.
Sitemaps
Select canonical URLs for all subpages and submit them in the sitemap. All pages listed in the sitemap are treated as canonical. If their content is similar, Google will decide which ones are duplicates.
Although it can’t be stated for sure that URLs from the sitemap will be considered canonicals, it’s a simple way to define canonical tags for sizable websites. Apart from that, the sitemap allows you to inform Google which subpages of your website are the most important in your opinion.
If you benefit from the sitemap, provide there only canonical URLs.
Below you can check all the pros and cons of every method we just discussed.
Canonical URL – Best Practices
Duplicate content can be extremely dangerous to your website, therefore, it’s advisable to consider a few best practices that will allow you to implement your canonical URLs correctly:
- Canonicals can point to the current URL – rel=canonicals can be self-referential. In other words, if you have three subpages with the same content (A, B, C), but you want the C subpage to be the main one, you can put the tag pointing to C on the URL of this subpage).
- It’s always a good idea to put a canonical tag on your home page, as it’s a kind of your business card and people may link to it from various locations you can’t control. This way, you can avoid potential problems.
- Stay transparent – if you send mixed signals, the search engine may have issues determining which URL is the canonical one. So, if you point from subpage A to subpage B and state that the latter one is your main subpage, then you shouldn’t point from subpage B to subpage A.
- Don’t canonicalize pages with similar content – rel=canonicals are dedicated to subpages with the same content. Nevertheless, many people feel tempted to apply them also on subpages with similar content. While this is acceptable when talking about various versions of the same product that differ in terms of color, or size, it’s worth keeping in mind that the tagged pages may not be included in the ranking. And if it turns out that the content differs too much, search engine robots won’t take rel canonicals into account.
Rel Canonicals – Common Mistakes
Since we’ve provided you with useful tips, now it’s time to discuss common mistakes that may occur when implementing rel canonicals:
- It’s not acceptable to canonicalize a paginated archive to your main page. The rel=canonical on subpage A should point to subpage A. Otherwise, search engine robots won’t index archive pages.
- Keep your canonicals transparent and specific, make sure you determine elements like HTTP or HTTPS.
- Avoid multiple rel canonicals. This mistake frequently occurs when you use SEO plugins. It’s crucial to avoid such situations, as multiple rel=canonicals may be a sign for Google that it should ignore all canonicals.
When Are Canonical Links Not a Necessity?
Although canonicals bring numerous benefits to your website, they aren’t always a necessity. It’s not obligatory to implement them in the following situations:
- If there are no URLs duplicating the content entirely or partially, there’s no need for canonical URLs. You don’t need a canonical link for a page to be ranked in SERPs – Google robots will crawl your website anyway.
- Properly implemented 301 redirects may also reduce the need for rel=canonical tags.
- Canonical tags are obligatory mainly if you have an on-site robots.txt file. In that file, you can find a list of URLs not indexed by the search engine. There, you can clearly indicate the pages that shouldn’t be indexed or displayed in the search results.
Try not to overdo the canonicalization on your site. Remember that Google needs to see your website as a valuable source of content. In order for this to happen, you need a sufficient amount of such quality content.
If internal duplicate content on your website doesn’t result from technical errors and the abovementioned solutions don’t bring the intended results, it’s always better to saturate the page with quality content created from scratch than to canonicalize. The latter may decrease the content-to-code ratio of the page, which may have a negative impact on your positions in the ranking.
Keep in mind that if you implement rel=canonicals incorrectly, Google crawlers will simply ignore them and the modifications won’t bring any improvements.
What is Rel Canonical – The Takeaway
Even if you don’t think there’s any duplicate content on your website, be sure to check this parameter and take appropriate steps if it turns out that your texts need to be improved. To keep Google penalties at bay, you may benefit from canonical tags. They come in handy when fighting any unintentional content duplication and help to boost your positions in the ranking. Properly implemented changes should quickly translate into increased traffic and conversions.